First Aid Treatment for Burns & Scalds

Injury
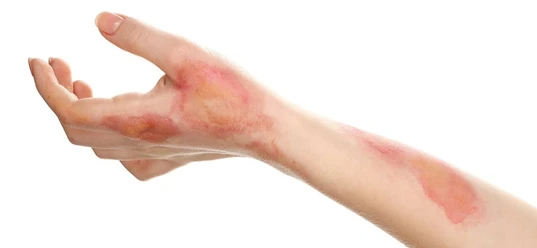
Treatment for burns and scalds is an important part of First Aid training. It can mean the difference between life and death in the case of life threatening burns.
Superficial burns or scalds affect the outer layer of your skin, causing redness and pain, sometimes blistering. Deeper burns often exhibit mottled shades of red and white, also with blisters on the skin, and the pain is also pronounced. Extreme burns — known as full thickness burns — cause damage all the way to the layer of fat beneath the skinWhat's the difference between a scald and a burn?
A scald is tissue damage caused by hot water. A burn is tissue damage from a more direct heat source, such as a stove or an iron, or the sun. It can also be caused by contact with electricity, or chemicals. Burns and scalds can result from a wide range of causes. Some common ones include:- Scalds can result from accident spills from hot beverages, kettles, and pots
- Burns after direct contact with heated objects, such as irons, hair straighteners, stoves, BBQ coals, or an open fire
- Burns from skin contact with dangerous chemicals, such as bleach or oven cleaner, or swallowing drain cleaner, etc
- Burns from direct contact with exposed electrical wires, old wires and faulty appliances, as well as cutting live cables
Symptoms of burns and scalds
Superficial burns or scalds affect the outer layer of your skin, causing redness and pain, sometimes blistering. Deeper burns often exhibit mottled shades of red and white, also with blisters on the skin, and the pain is also pronounced. Extreme burns — known as full thickness burns — cause damage all the way to the layer of fat beneath the skin. They can appear brown, white or even black, and have a leathery and dry feel to the touch. A full thickness burn can damage or destroy nerve cells, so pain might not be felt.What First Aid is best for burns or scalds?
Step 1: Remove the source of the burn
If fire is the source, roll the victim on the ground to snuff out the fire. If a fire blanket is available, use it to cover the person and suffocate the flames. If the source is an electrical current, turn off the power. When chemicals are the cause, remove contaminated clothing and apply water to the affected area. If the chemical burn has been caused by dry chemicals, first brush off the chemicals before applying water to the area.Step 2: Cool the burn
With all burns and scalds, run cool water over the skin for a minimum of 20 minutes. This is critical to stop the burn becoming worse. Never use ice on a burn, just water. Remove clothing that’s near the burn but, if any clothing that is stuck to the burn should not be removed.Step 3: Cover the burn
After running cool water over it, cover the burn with a light, non-stick dressing. Avoid using any material that is fluffy. Cling-wrap plastic makes a great cover. For burns on an arm or leg, raise the limb up to help reduce swelling.When do I call an ambulance?
Call an ambulance or go straight to the emergency department if the any of the following has occurred:- Burn is deep — nerves may be damaged if the victim is feeling no pain
- Burn is larger than a 20 cent piece
- Burns involve the genitals, airways, face, or hands
- Skin is dry and leathery where burnt
- Skin has white, black or brown patches
- Burns involve electricity or chemicals
- Victim is struggling to breathe
Avoid this when treating a burn?
- Do not apply lotions and creams – these can seal in heat
- Do not pop any blisters caused by a burn
- Avoid touching the burn
- Do not use ice
- Do not place a child in a cold bath — this may lead to shock
How to prevent burns or scalds
Tips to prevent burns or scalds occurring in the home:- Always keep hot liquids out of reach of children
- Keep pot or pan handles facing inwards on stoves
- Be careful with electrical items & unplug them after use
- Install smoke detectors & have them tested regularly
- Keep a fire extinguisher
- Use protective clothing when using chemicals
- Keep hot water system thermostats below 50°
Originally published at
https://www.australiawidefirstaid.com.au/resources/first-aid-treatment-for-burns-scalds
as part of the Australia Wide First Aid Articles Library